Scientific Calculator on BREW "psec" - 4 / 7 -
4. Functions
4.1. Correspondence of Functions and the Virtual Keyboard
Pressing "OPE", followed by the "FNC" key toggles to the virtual keyboard for inputting functions.
The diagram below depicts the virtual keyboards containing functions, and their interrelations.
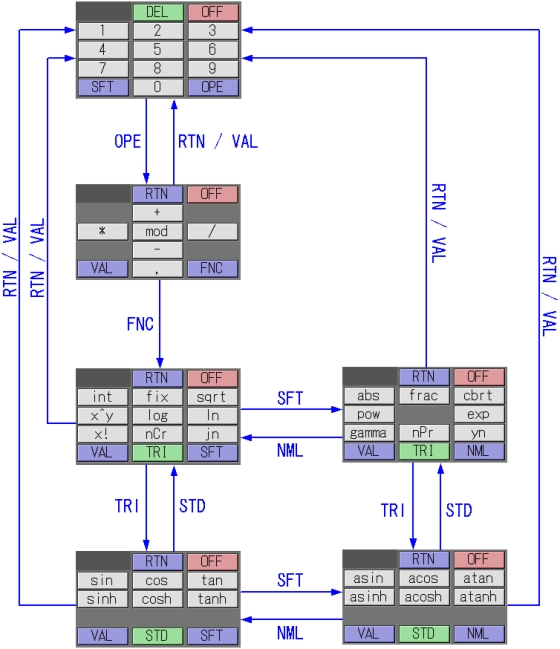
4.2. Functions Details
The tables below are lists of functions that can be used in psec.
* x and y represents real numbers, n and r represents integers.
Arithmetic Operators
| Name | Meaning | Example | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Input | Output | ||
| x! (displayed as !) | Calculates factorial of x .
When used twice, it means double factorial. In case of double factorial, x must be an integer > 0. "-12!" will be interpreted as "-(12!). |
3.5! | 11.631728396568 |
| 6!! | 48 | ||
| x^y (displayed as ^) | Calculate xy | 2^10 | 1024 |
| nPr | Calculate permutation nPr. r should be 0 ≤ r ≤ n . |
7nPr3 | 210 |
| nCr | Calculate combination nCr. r should be 0 ≤ r ≤ n |
7nCr3 | 35 |
Standard Functions
| Name | Meaning | Example | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Input | Output | ||
| abs(x) | Calculate |x| | abs(-3.5) | 3.5 |
| cbrt(x) | Calculate third root of x | 8 | 2 |
| fix(x) | Get integer part of x When x < 0 , the answer will be larger than x. |
fix(3.5) | 3 |
| fix(-3.5) | -3 | ||
| frac(x) | Get decimal part of x When x < 0 , answer will be "-" and the decimal part of |x| . |
frac(3.2) | 0.2 |
| frac(-3.2) | -0.2 | ||
| int(x) | Get integer part of x When x < 0 , answer will be smaller than x. |
int(3.5) | 3 |
| int(-3.5) | -4 | ||
| sqrt(x) | Calculate root x x must be x ≥ 0 |
sqrt(36) | 6 |
| Name | Meaning | Example | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Input | Output | ||
| exp(x) | Calculate ex | exp(-1) | 0.3678794411714 |
| ln(x) | Calculate logex x must be x > 0 |
ln(10) | 2.3025850929941 |
| log(x) | Calculate log10x x must be x > 0 |
log(10) | 1 |
| pow(x, y) | Calculate xy | pow(2, 10) | 1024 |
Trigonometric / Inverse Trigonometric / Hyperbolic / Arc Hyperbolic Functions
Trigonometric functions (sin, cos, tan) interpret the argument according to the chosen angular mode ( Deg, Rad, Gra).
For example, "sin(30)" will be interpreted as "sin(30°) in the Deg mode, but in Rad mode, it will be interpreted as "sin(30 rad).
Function domains are the same as in mathematics.
| Name | Meaning |
|---|---|
| acos(x) | cos-1(x) |
| acosh(x) | cosh-1(x) |
| asin(x) | sin-1(x) |
| asinh(x) | sinh-1(x) |
| atan(x) | tan-1(x) |
| atanh(x) | tanh-1(x) |
| cos(x) | cos(x) |
| cosh(x) | cosh(x) |
| sin(x) | sin(x) |
| sinh(x) | sinh(x) |
| tan(x) | tan(x) |
| tanh(x) | tanh(x) |
Special Functions
Function domains are the same as in mathematics.
| Name | Meaning | Example | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Input | Output | ||
| gamma(x) | gamma(3) | 2 | |
| jn(n, x) | 1st type of Bessel functions of n th order Jn(x) | jn(3, 2.5) | 0.2166003910391 |
| yn(n, x) | 2nd type of Bessel functions of n th order Yn(x) | yn(3, 2.5) | -0.756055496754 |







